https://www.washingtonpost.com/investigations/2020/12/11/coronavirus-airborne-video-infrared-spread/

The virus spreads most commonly through close contact, scientists say. But under certain conditions, people farther than six feet apart can become infected by exposure to tiny droplets and particles exhaled by an infected person, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention said in October. Those droplets and particles can linger in the air for minutes to hours.
To visually illustrate the risk of airborne transmission in real time, The Washington Post used an infrared camera made by the company FLIR Systems that is capable of detecting exhaled breath. Numerous experts — epidemiologists, virologists and engineers — supported the notion of using exhalation as a conservative proxy to show potential transmission risk in various settings.
“The images are very, very telling,” said Rajat Mittal, a professor of mechanical engineering in Johns Hopkins University’s medical and engineering schools and an expert on virus transmission. “Getting two people and actually visualizing what’s happening between them, that’s very invaluable.”
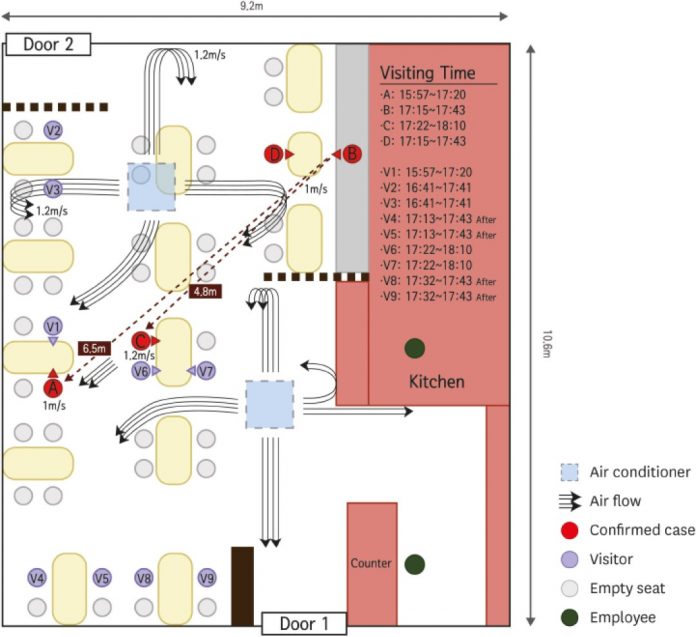
https://www.washingtonpost.com/food/2020/12/11/korean-restaurant-coronavirus-airflow-study/
The study appears to be more bad news for restaurants, which have already been identified in research as a primary source for the spread of the virus. The Korean researchers recommend that public health authorities update safety guidelines based on their study, arguing that six feet of space between tables is not enough to protect diners from being infected.